Ecological Pyramid
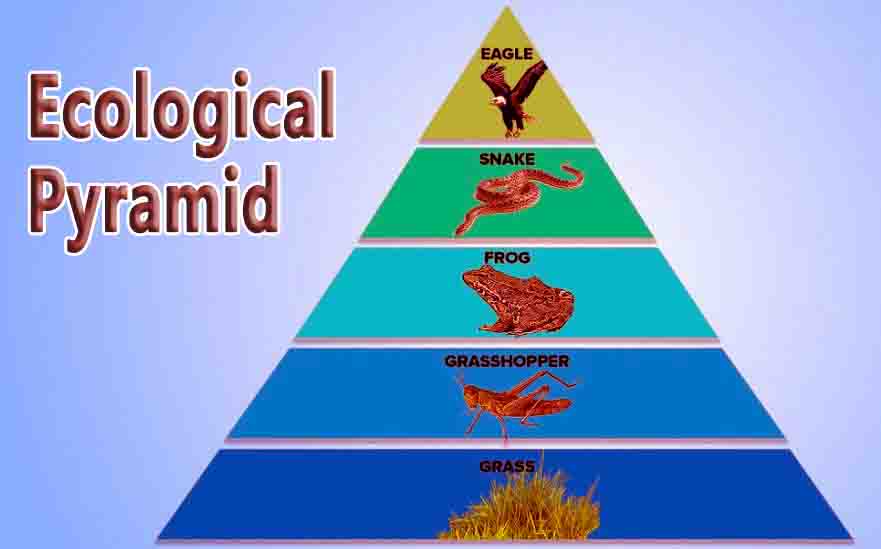
Ecological Pyramid Definition An ecological pyramid is a graphical representation of the relationship between different organisms in an ecosystem. Each of the bars that make up the pyramid represents a different trophic level, and their order, which is based on who eats whom, represents the flow of energy. Energy moves up the pyramid, starting with … Read more